Create a Scheduled Task to Run PowerShell Script
Requirement: Schedule PowerShell Script in Windows Task Scheduler.
PowerShell is really a game-changer to automate repetitive or time-consuming processes, isn’t it? We have a PowerShell script to generate a report on SharePoint content database size growth – Storage Report; we used to run it on the first day of every month on the SharePoint server to generate the report. Why don’t we automate it with the Windows Task Scheduler? Sure! Let’s create a scheduled task for the PowerShell script with the Microsoft Windows task scheduler in Windows Server 2008/2012 R2. In this blog post, I’ll show you how to create a Scheduled task to run a PowerShell script using the Windows Task Scheduler step-by-step.
How to Create a Scheduled Task for PowerShell Script with Windows Task Scheduler?
Combining the flexibility of PowerShell with the scheduling capabilities of Task Scheduler opens up a world of possibilities for automating repetitive tasks and running maintenance scripts. You can automate your PowerShell scripts with the Windows task scheduler. To schedule a SharePoint PowerShell script to run in Task Scheduler, ensure you have the necessary PowerShell modules, such as “Microsoft.SharePoint.PowerShell” or PnP.PowerShell is installed on the machine first. Then proceed with the below steps to create a scheduled task for the SharePoint PowerShell script:
Task Scheduler is a built-in utility in Windows that allows you to create and manage automated tasks. These tasks can be triggered based on various criteria, such as a specific time, system startup, or even a particular event. Here is how you can create a Scheduled Task manually:
- Open the Task Scheduler by going to Start Menu >> Administrative Tools >> Task Scheduler.
- From the Actions menu, click on “Create a Basic Task”.
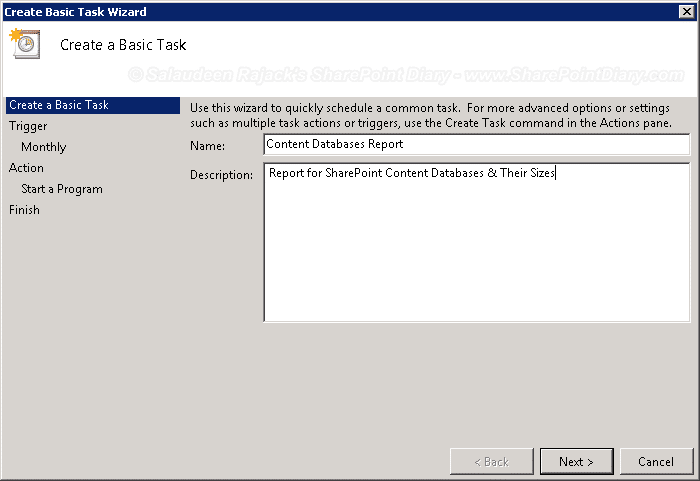
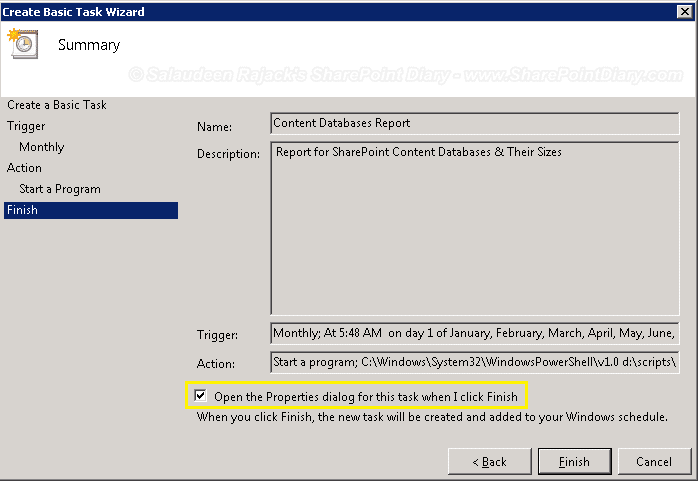
- Please give it a Name and Description. Say: “Content Databases Report”, and click “Next”.
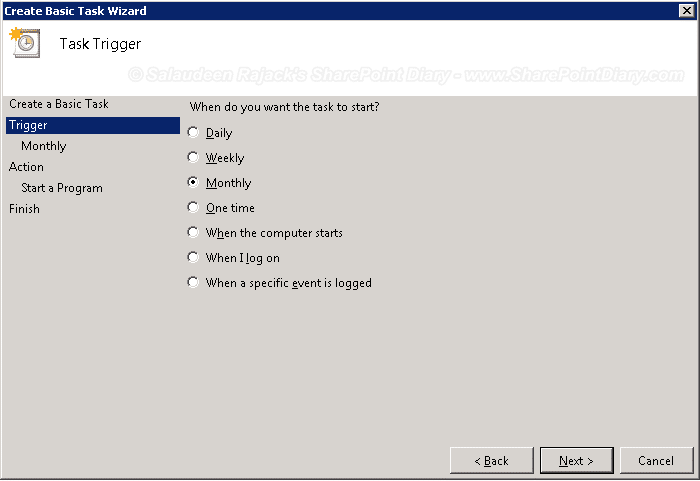
- On the Triggers tab, Select the interval you want to run the program, such as “Daily”, “Weekly”, etc. In my case, I chose “Monthly”.
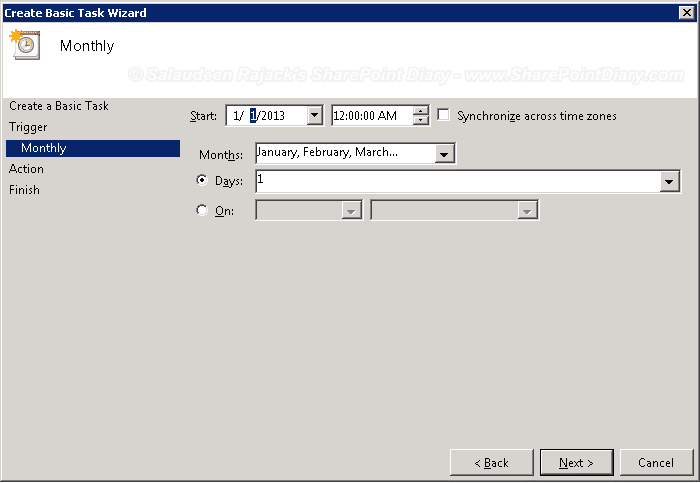
- Specify the Months and days in which the script is to run. I’ve selected “All Months” and Day 1.
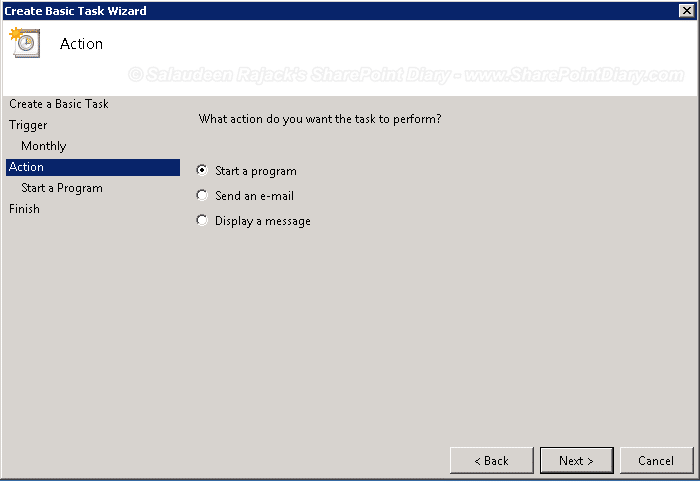
- In the Action Tab, choose what action you want the task to perform. For our purposes, we’ll select the “Start a program” option button. Click Next.
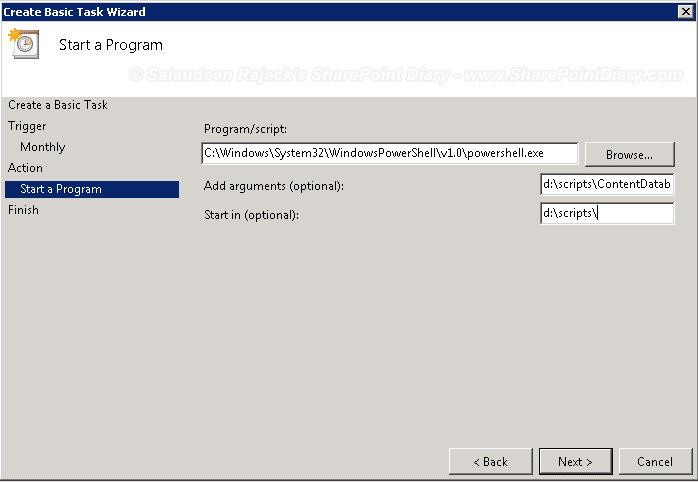
- In the “Start a Program” Tab:
- In Program/script, Enter the path of the Windows PowerShell: C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
- In Arguments, Enter the path of the script. Say: D:\Scripts\ContentDatabaseReport.ps1
- In “Start in”, Enter the folder path where the script is located. Say “D:\Scripts”
Important: You must specify a value for the Start-in field, even though it’s optional. This is because if no value is specified, PowerShell exports the output in the “C:\Windows\System32” directory.
- Select the checkbox “Open the Properties dialog for this task when I click Finish”, and click the Finish button.
- In the properties dialog, under the General tab, ensure that the “Run when user is logged on or not” and “Run with highest privileges” checkboxes are selected to ensure you are running the script with Administrator rights.
- You will get a login prompt by clicking the “OK” button. Confirm the User Name & Password in which the task runs (preferably, a service account with a password never expires flag set) and press enter. The task scheduler will create a new task to run the PowerShell script on given parameters.
You can use this method to schedule SharePoint Online PowerShell scripts as well. Just make sure you have the required modules, such as PnP PowerShell or SharePoint Online PowerShell modules, installed before scheduling them in the Windows task scheduler.
Create Tasks in the Task Scheduler Command Line:
We can add a PowerShell script to the task scheduler with the command line tool schtasks, too! Use the following command:
schtasks /create /TN "Content Database Report" /SC monthly /mo 1 /ST 00:00 /RU "Domain\UserName" /RP "Password" /RL "HIGHEST" /TR "PowerShell D:\Scripts\ContentDatabaseReport.ps1"
This will set the options “Run with highest privileges” and “Run whether the user is logged on or not” for the Scheduled Task.
Run the Scheduled Task on demand:
To run a PowerShell script from the task scheduler,
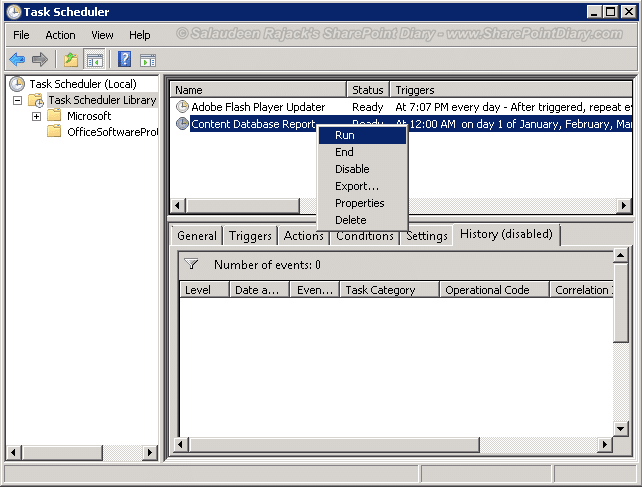
- Open task scheduler >> Browse to “Task scheduler Library” >> Right-click on the created task and choose Run.
- Switch over to the script file location and verify a new report has been generated as an output from the script.
That’s all! We’ve created a task in the Windows task scheduler for the PowerShell script!
PowerShell script with parameters in a scheduled task:
Say, We have a Parameter “$WebAppURL” in our PowerShell script: Param( [parameter(Mandatory=$true)] $WebAppURL), then we should trigger the script as: .\StorageReport.ps1 "https://sharepoint.crescent.com"
So in the Task scheduler, Add arguments (optional), Enter d:\scripts\StorageReport.ps1 "https://sharepoint.crescent.com"
When there are multiple parameters, you can separate them by giving the parameter name as the key. Such as:
Param(
[parameter(Mandatory=$true)] $WebAppURL,
[parameter(Mandatory=$true)] $OutPut
)
We trigger it as: StorageReport.ps1 -WebAppURL "https://sharepoint.crescent.com" -output "d:\Reports\StorageReport.csv"
“C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe” -command “<Your PowerShell Script Location>”
Create Scheduled Tasks with PowerShell:
From PowerShell 3.0 (Windows Server 2012 R2) onwards, we have PowerShell cmdlets to manage tasks in the Task scheduler. While the GUI is user-friendly, you can also create, delete, enable, or disable tasks using PowerShell.
Use Register-ScheduledTask to create a Scheduled Task! Here is an example:
This code snippet creates a new scheduled task named “Audit Large Lists” that runs daily at 1 AM, executing the specified PowerShell script.
#Variables
$TaskName = "Audit Large Lists"
$username ="Crescent\SP13_FarmAdmin"
$password ="Password Here"
#create a scheduled task with powershell
$Action = New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute "PowerShell.exe" -Argument "E:\Scripts\AuditLists.ps1"
$Trigger = New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -Daily -At 1am
$ScheduledTask = New-ScheduledTask -Action $action -Trigger $trigger
Register-ScheduledTask -TaskName $TaskName -InputObject $ScheduledTask -User $username -Password $password
Enter the parameters for the task you want to create, including the task name, action (this is what you want the task to do), trigger (when you want the task to run), user name, and password. Once you have entered all this information, execute the script, and the task will be created! To create and Manage Scheduled Tasks using PowerShell, refer: How to Create a Scheduled Task using PowerShell?
Troubleshoot a scheduled task running a PowerShell script
If a scheduled task running a PowerShell script is not working as expected, you can try the following:
- Check the Task Scheduler event logs in the Event Viewer for any error messages or relevant information.
- Verify that the PowerShell script path and parameters specified in the task action are correct.
- Ensure the Script execution policies are not preventing the script from running (Set it to:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned). - Ensure that the user account under which the task runs has the necessary permissions to execute the script.
- Test the PowerShell script manually in a PowerShell console to see if it runs without errors.
- Enable logging or add logging statements within your PowerShell script to capture relevant information (e.g., Start-Transcript and Stop-Transcript).
Wrapping up
Creating a scheduled task to run a PowerShell script using Windows Task Scheduler is a great way to automate repetitive tasks. Using a scheduled task to run a PowerShell script can help automate repetitive tasks, ensure consistency and accuracy in task execution, and save time and resources. It can also allow for more efficient use of system resources by scheduling tasks to run during off-peak hours.
By following the steps above, you can quickly get started with setting up your own scheduled tasks. You can also schedule a PowerShell script with Azure Automation! SharePoint Online: How to Schedule a PowerShell Script using Azure Automation?
Open Task Scheduler >> Create a Basic Task >> Provide a Name to your Task >> Set the trigger to run the task daily or at a specific time. Set the action to “Start a program”. In the “Program/script” field, enter the path to PowerShell.exe: “C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe“. In the “Add arguments” field, enter the path to your PowerShell script: “-File C:\Path\To\Your\Script.ps1“. Click “OK” to save the task.
To run a PowerShell script with elevated privileges from Task Scheduler, in Task properties – select the “Run with highest privileges” option under the General tab!
Use the Register-ScheduledTask cmdlet to create a new scheduled task on the computer, passing the trigger and action as parameters. E.g.,$Trigger = New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -Daily -At 10am
$Action = New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute "Powershell.exe" -Argument "D:\Scripts\ReportGen.ps1"
Register-ScheduledTask -TaskName "Execute Report Gen Powershell" -Trigger $Trigger -Action $Action
To receive email notifications for the status of a scheduled PowerShell script, you can add email notification functionality within your PowerShell script. Use the Send-MailMessage cmdlet to send an email with the relevant information, such as the script’s status, output, or any errors encountered. Configure the email settings, such as the SMTP server, sender, and recipient details, within your script or using a configuration file.
Yes, you can schedule a PowerShell script to run as a different user by modifying the security options of the scheduled task. In the “General” tab of the task properties, click “Change User or Group” and enter the desired user account under which the task should run. Make sure the specified user has the necessary permissions to execute the script.
To schedule a PowerShell script to run at a specific time, you can configure the task trigger accordingly. In the “Triggers” tab of the task properties, click “New” and select “Daily” or “Weekly” as the trigger type. Set the desired start time and recurrence pattern for when the script should run.
To run a PowerShell script with parameters as a scheduled task, you can modify the “Add arguments” field in the task action. For example:-File "C:\path\to\your\script.ps1" -Parameter1 Value1 -Parameter2 Value2
Replace Parameter1 and Parameter2 with the actual parameter names and provide the corresponding values.
Create a new task in Task Scheduler >> In the “Triggers” tab, select “New” and choose “At startup” from the “Begin the task” dropdown >> Configure the action to run your PowerShell script as described earlier.
To modify a scheduled task to run the PowerShell script, you can open the Task Scheduler and edit the properties of the task. You can change the trigger, action, and other settings as needed. To delete a scheduled task, you can right-click on the task in the Task Scheduler and select Delete.